A parasitic infection is called helminthiasis. This is a dangerous and common disease that has not been noticed for many years. Parasites enter the human intestine through dirty hands, food, water and begin to multiply actively.
They absorb nutrients, interfere with the absorption of water and vitamins in the intestine, provoke diarrhea and disorders of other internal organs. Therefore, it is very important to know what tests to do for parasites to identify in a timely manner and begin proper treatment.
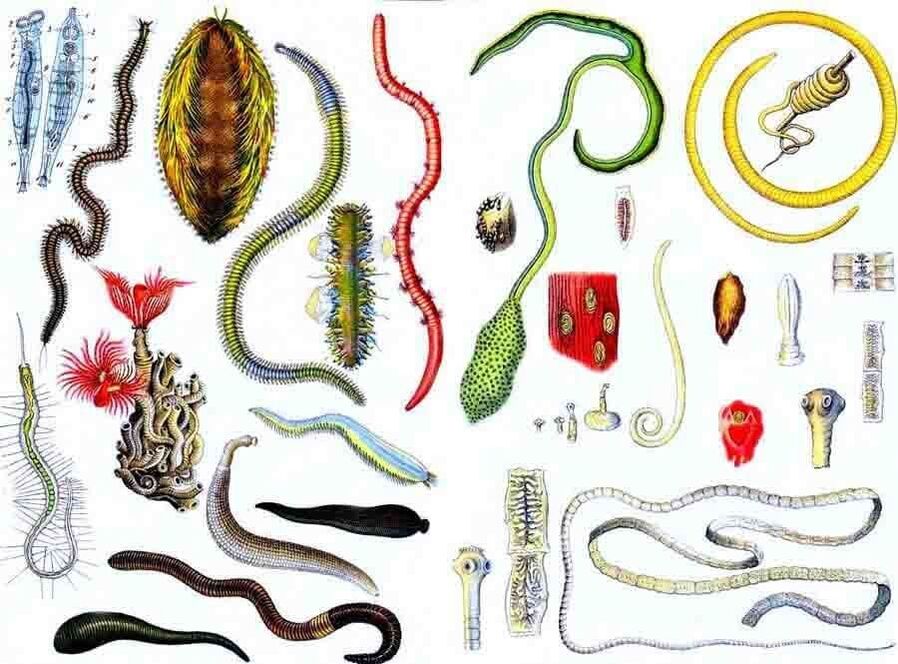

Types of parasites and their diagnostics
Various types of worms can live in the human intestine: round, flat tape. Any parasite is harmful to the body, as it releases toxic substances that affect internal organs.
The consequences of helminthiasis can be very different, including death.
Everyone should know what tests to do for parasites. Examination is performed both for preventive purposes and in the presence of characteristic symptoms. Do not delay your visit to the doctor.
The danger of this condition is that symptoms do not always appear. For a long time, one may not be aware of the presence of helminths, but at the same time, a slow and irreversible process of destruction occurs in the organs. The path of infection is very different: contact with an infected person or animal, through hands, soil, food, dirty water.
| Title | Path of infection | Symptoms | Analyze |
| Pinworms | Pollution through dirty hands | Itching in the anus, diarrhea, weight loss | Anal swab |
| Ascaris | Eat unwashed vegetables and fruits | Weakness, itching in the anus, disturbed stools | Antibody Blood Test (ELISA) |
| Cat Fluke | Eating Contaminated Fish | Pain in the right side, allergic reactions, signs of liver damage | ELISA blood test |
| Trichinella | Eat contaminated pork and lard | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic skin reactions, weakness | Antibody Blood Test |
| Intestinal acne | Any contact with contaminated soil | Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain | Stool study for worm eggs, ELISA analysis |
Treatment of helminthiasis is individually selected. Before prescribing any medication, your doctor will advise you to have a test and determine the exact type of parasite. Each individual helminth has a different effect on the body and leads to different complications. Theoretically, they can affect any organ, but are more often localized in the gut. Risk groups include young children and people working with land.
The main and dangerous signs of parasitic infection
It is difficult to recognize an infection. Symptoms are affected not only by the type of helminths, but also by the age of the infected person, the state of his immune system and other body characteristics. Due to the decrease in immunity in children and the elderly, the clinical picture is more acute.
There are chronic helminthiases that have no obvious acute signs and manifestations. They last for years and go unnoticed because their symptoms are vague and easily confused with other chronic conditions.
See a doctor immediately and be tested for parasites when the following symptoms appear:
| Sign | Clinical presentation |
| Increased body temperature | These symptoms do not always occur, but with severe damage to internal organs, the temperature can be high, leading to fever. |
| Stool Disorders | With helminthiasis, constipation and diarrhea are observed. Various bowel disorders can change, increase or disappear over time. In feces, mucus and blood feces are often found. |
| Nausea and vomiting | Symptoms of poisoning appear in the acute form of the disease. These symptoms can occur with any parasitic attack. |
| Cough | With prolonged disease, helminths affect the bronchi and lungs. The patient experiences tuberculosis, eventually turning wet. |
| Allergies | The immune system begins to respond to parasites, so allergic reactions occur, usually skin reactions: itching, redness, itching. |
| Chronic fatigue | Helminthiasis causes weakness and fatigue, drowsiness due to body intoxication. |
| Weight Loss | Due to intestinal absorption disorders, a person loses weight even with the same diet. |
Regardless of where the worms live in the gut, treatment should be started as early as possible. Parasites cause inflammation of the intestines, penetrating the lungs, gallbladder and even the heart. Preventive screening will help avoid serious consequences and complications.
Ready for blood and stool tests
The reliability of the results depends not only on the laboratory and equipment, but also on compliance with the rules of preparation. Violation of this rule will result in a wrong decision. The person may be immune to the disease.
First of all, keep in mind that to assess the situation you need to choose a proven clinic, a reliable laboratory where certified specialists work. If the examination is done by a doctor, he or she will warn about the preparation.
Preparations for stool analysis include the following:
- A few days before the birth of stool, you need to adhere to a gentle diet, do not eat spicy, fried, fast food and foods that cause bloating. It is recommended to eat cereals, soups, low-fat dairy products.
- If you can not go to the bathroom, you can not give an enema or take laxatives.
- It is not recommended to eat food that stains feces: prunes, tomatoes, beets, herbs.
- Before taking the test, you need to buy a sterile container with a special spatula. It is printed on test day. Matchboxes should not be used to collect materials.
- The minimum amount of feces required for analysis is 15 g. If the number is less, the analysis should be repeated.
- Collect the ingredients carefully so that no urine or menstrual flow enters the stool.
- If the analysis shows the presence of helminths, upon completion of treatment, the analysis must be repeated, complying with all of the above rules.
Preparation for donations is usually standard. You should visit the laboratory on an empty stomach, do not eat fatty or spicy foods the day before. Any medication you take should be discussed with your doctor, as it can affect parasitic test results. It is recommended to stop drinking alcohol a week before donating blood. On the day of the blood sample and the day before, you could not follow the physiotherapy procedure, undergoing an ultrasound examination. Smoking can also affect the results. It is best not to smoke at least an hour before the exam.
Blood test for parasites
Blood tests for parasites are one of the most informative methods for diagnosing helminthiasis. There are several types of blood tests. The doctor prescribes one or more, depending on the clinical picture and the anamnesis.
The advantage of blood tests from fecal analysis for helminths is that eggs are not always found in feces, you need to enter the breeding time of certain helminths. Blood can be donated at any time of infection. Almost all laboratory analyzes are performed using special equipment and do not depend on human factors. ELISA allows you to determine not only the worm, but also the degree of infection.
The doctor should be responsible for decoding the results. The most common are 3 blood tests to determine the worms in the body:
| Method | Analysis Features |
| ELISA | ELISA is the most informative and reliable in determining parasitic infections. Examination is made based on the antigen-antibody relationship. The results indicate the presence or absence of specific antibodies in the blood, indicating the degree of acute or chronic disease. Thus, with parasitic lesions, IgG antibodies appear in the blood. The results are quite simple, positive or negative. However, it must be remembered that these antibodies appear in chronic infections and during recovery. |
| PCR | The polymerase chain reaction also allows you to determine with certainty whether there are parasites in the body. However, not all types of helminths are determined in this way, but only protozoa. The severity of the disease and the number of helminths can also not be determined in this way. |
| UAC | This is a simple and quick diagnosis that gives an idea of how the body functions as a whole. The presence of parasites can be suspected by eosinophil levels, which will increase. With helminthic invasion, eosinophil levels exceed 20% of the remaining leukocytes. In this case, further examination and determination of the type of parasite is prescribed. |

Bench Parasite Test
Coprogram is a laboratory test for feces. It is prescribed if there is a suspicion of helminthiasis: stool disorders, sudden weight loss, weakness, nausea, etc. You can take a coprogram at any lab: private or city.
The following instructions are taken into account in decoding:
| Metrics | Decryption |
| Consistency and smell | Normal consistency is viscous without undigested pieces. |
| Color | Usually, the color is yellow or brown. Or too dark, this indicates the presence of hidden blood. Bright colored stools show liver damage. |
| Weight | The presence of blood or mucus in the stool is taken into account. |
| Leukocytes | Leukocytes are usually present in the feces, but in minimal amounts. If there are many of them, then the inflammatory process has started in the intestine. |
| Acidity | The feces of healthy people have a pH of 4. 8-5. 8. If the acidity increases, then the absorption of fatty acids is disrupted in the intestine. |
| Bilirubin | There is no bilirubin in the feces of healthy people. Its presence indicates the presence of dysbiosis, increased peristalsis, rapid bowel movements. |
| Stercobilin | This enzyme can be found in feces up to 350 mg / day. An increase indicates anemia, a decrease indicates a lesion on the gallbladder. |
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on these results. Further testing may be required. In order for the results to be reliable, you need to collect and store the material properly. It is best to bring it to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Eroding enterobiasis
Scraping enterobiasis is also an information diagnosis. It is delivered according to instructions or for prevention. This is a painless procedure. Using a small spatula or cotton, take some ingredients from the anus. Enough to swipe the stick a few times to get the ingredients.
Scraping is relatively easy - worm eggs do not exist or do not exist. The disease can be overcome, but if the result is positive, the patient is isolated to prevent further transmission of the infection.